Resources
House, S (1997): A introduction to teaching english to children. London: Richmond.Scott, W., Ytreberg, L. (1991): Teaching english to children. London: Longman.
Moon, J. (2000): Children lerning english. Oxford: Macmillan Heinemann.
7. CLIL (Content and Language Integrated Learning)
7.1. What is CLIL? (incluye los objetivos: aim)
As indicated by the acronym CLIL “Content and Language
Integrated Learning” in which pupils learn a subjects through the medium of a
foreign language.
CLIC has reference situations where students are taught
through a foreign language with dual-focused aim, namely the learning of
content, and the simultaneous learning of a foreign language.
There are several model of CLIL:
- “Integrated” or “embedded”:
primary pupils experiment with elements of the TL.
- Meanings that matter: attractive
topic and age appropriate. In addition, work with other schools, students….
- Bilingual or immersion learning:
teaching a topic in a style that includes learning another language.
The aims
which expect to achieve are
1. Obtain knowledge target language.
2. Attain necessary skills in the target language.
3. Acquire necessary skills in the mother tongue.
4. Comprehend and respect both cultures.
5. Develop cognitive and social skills
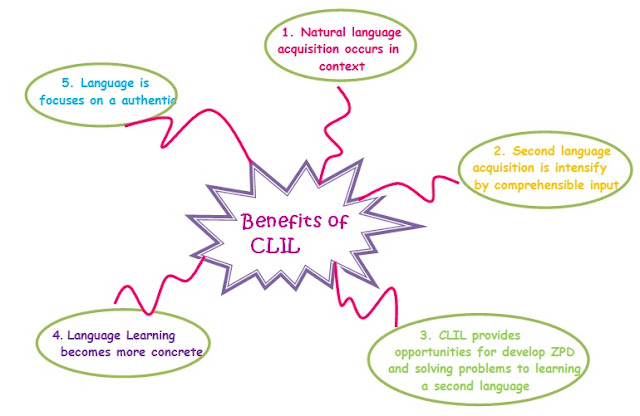
Benefits
In other words:
- Naturalistic learning.
- Meaningful and real communication
- Primacy of meaning over form
- Affective gains
- Communicative competence
Advantages
7.3. Characteristics and examples
CLIL lessons integrate language and skills and receptive and productive skills,
with reading and listening activities. The language is functional and
determined by the context of the subject, and is approached lexically
rather grammatically.
Also, there are 4 important charasterictis that have to be present all the time in the CLIL Methodology. It is:
- Communication: Using language to learn whilst learning to use language

- Content: Progression in knowledge, skills and understanding related to specific elements of a defined curriculum.

- Culture: Exposure to alternative perspectives and shared understandings, which deepen awareness of otherness and self.

- Cognitive:Developing thinking skills which link concept formation (abstract and concrete), understanding and language.